電子顕微鏡 Electron microscope
設置機器メーカー/型式 Equipment
- 透過型電子顕微鏡 Transmission Electron Microscope HT7800
- 電界放出形走査電子顕微鏡 Field emission scanning electron microscope JSM-7505FA
- 走査型電子顕微鏡 Scanning electron microscope JSM-6010LA
電子顕微鏡とは What is an electron microscope?
電子顕微鏡は、電子線を用いて試料の拡大像を観察する装置です。同じ目的を持った装置に光学顕微鏡がありますが、電子顕微鏡の方が高倍率で像を観察することができます。これは、光学顕微鏡が光源に可視光線を用いて像を観察するのに対し、電子顕微鏡では可視光線に比べてはるかに波長の短い電子線を用いているためです。したがって、光学顕微鏡で用いるガラスレンズの代わりに、電子顕微鏡では電子レンズを用います。電子線は空気中を進むことができませんので、電子線の通路である鏡体内は高真空に保たれています。
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses an electron beam to observe a magnified image of a sample. An optical microscope is a microscope with the same purpose, but the electron microscope can provide observation at higher magnification. This is because optical microscopes use visible light as a light source to observe images, whereas electron microscopes use electron beams, which have a much shorter wavelength than visible light. Therefore, electron microscopes use electron lenses instead of the glass lenses used in optical microscopes. Since electron beams cannot travel through air, the inside of the mirror body through which they pass is maintained to a high vacuum.
透過型電子顕微鏡と走査型電子顕微鏡
Transmission electron microscope and scanning electron microscope
電子顕微鏡には、透過型電子顕微鏡(TEM:Transmission Electron Microscope)と走査型電子顕微鏡(SEM:Scanning Electron Microscope)があります。両者の違いは、TEMでは厚さ0.1ミクロン以下に薄切した試料に電子線をあて、試料を透過した電子により像を得て内部構造を観察するのに対し、SEMでは試料面上を電子線で走査し、そこから得られる二次電子や反射電子を用いて表面構造を観察するという点にあります。
There are two types of electron microscopes: transmission electron microscope (TEM) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). TEM uses a high voltage electron beam to create an image. The electron beam is transmitted through a thin section less than 0.1 micron that is in part transparent to electrons and in part scatters them out of the beam. When it emerges from the sample, the electron beam carries information about the structure of the sample that is magnified by the objective lens system of the microscope. Unlike TEM, where electrons of the high voltage beam carry the image of the sample, SEM scans a sample surface with electron beams and obtains the secondary and reflected electrons to observe the surface structure.
透過型電子顕微鏡の構造 Structure of TEM
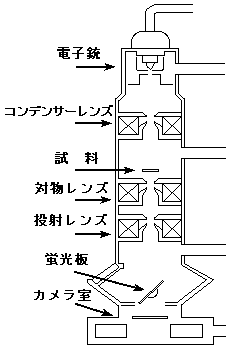 光源部である電子銃から発生した電子線は、コンデンサーレンズによって照射強度や照射面積を調整され試料を照射します。試料を透過した電子線は、対物レンズにより拡大、結像します。対物レンズによってできた像を、投射レンズでさらに拡大し、蛍光板上に投影して観察します。蛍光板の下にはカメラ室が設けてあり、ここで写真撮影を行い像を記録します。
光源部である電子銃から発生した電子線は、コンデンサーレンズによって照射強度や照射面積を調整され試料を照射します。試料を透過した電子線は、対物レンズにより拡大、結像します。対物レンズによってできた像を、投射レンズでさらに拡大し、蛍光板上に投影して観察します。蛍光板の下にはカメラ室が設けてあり、ここで写真撮影を行い像を記録します。
また、鏡体内は真空排気装置によって常に高真空に保たれています。
The electrons emitted by the electron gun is focused by the condenser lens and transmitted through the sample.
When it emerges from the sample, the electron beam carries information about the structure of the sample that is magnified by the objective lens. This information (the "image") is viewed by projecting the magnified electron image onto a fluorescent viewing screen. The image can be photographically recorded at the camera room located below the fluorescent viewing screen.
The inside of the mirror body is maintained to a high vacuum by a vacuum exhaust system
走査型電子顕微鏡の構造 Structure of SEM
光源部である電子銃から発生した電子線は、コンデンサーレンズで調整された後、対物レンズにより試料面上で小さなスポットになるように調整されて試料を照射します。
SEMでは、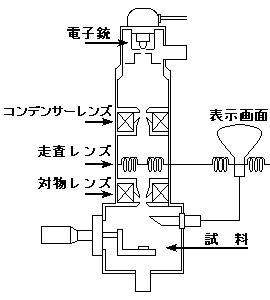 照射された点から発生した二次電子や反射電子を検出、増幅し、その量に応じた明るさを画面に表示します。このとき、電子線のスポットを走査コイルによって試料面上を走査させると同時に、表示画面上にこれと同期させて像を表示することにより拡大像を得ます。拡大像の記録には、写真撮影専用の画面にカメラをセットして撮影します。
照射された点から発生した二次電子や反射電子を検出、増幅し、その量に応じた明るさを画面に表示します。このとき、電子線のスポットを走査コイルによって試料面上を走査させると同時に、表示画面上にこれと同期させて像を表示することにより拡大像を得ます。拡大像の記録には、写真撮影専用の画面にカメラをセットして撮影します。
TEMと同様に鏡体内は真空排気装置によって常に高真空に保たれています。
The electrons emitted by the electron gun is focused by the condenser lens and adjusted by the objective lens to form a small spot on the sample surface, and then it is scanned across a rectangular area of the sample.
Signals such as secondary electrons and light emission at each point on the sample are detected and amplified, and at the same time, the display of the SEM maps the varying intensity of any of these signals into the image in a position corresponding to the position of the beam on the sample.
To record magnified images, the camera system is set on a photographic screen.
As with TEM, the inside of the mirror body is maintained to a high vacuum by a vacuum exhaust system.
試料について EM sample preparation
電子顕微鏡で観察する試料は、高真空に保たれた鏡体内に持ち込まれ、なおかつ、強力な電子線の照射を受けます。このため、充分に乾燥し、電子線による発熱や帯電を防ぐとともに、構造に関する必要かつ十分な情報を得られるようになっていなければなりません。特に、生物試料では、生きていた時の状態をできるだけ反映する像を得るために、試料の作製には様々な工夫がなされています。
Samples for electron microscopic observation are loaded into a high vacuum mirror body and irradiated with powerful electron beams. Therefore, they must be sufficiently dried to prevent heat and charging generated by the electron beam, as well as to provide necessary and enough information about the structure. Especially for biological samples, various measures are made for obtaining images that reflect the state of the sample when it was alive as much as possible.
TEMの試料作製 TEM sample preparation technique
TEMで試料を観察するには、試料は充分に薄くなければなりません。そこで、生物試料の作製に使われている超薄切片法について簡単に説明します。
- 観察する部位の組織を切り出し、グルタールアルデヒドや四酸化オスミウムなどで固定します。
- 水分を除くため、アルコールやアセトンを用いて脱水します。
- 脱水後の試料は、エポン等の樹脂で包埋し、0.1ミクロン以下の厚さに薄切します。
包埋したブロックはガラスナイフ(またはダイアモンドナイフ)を用いて薄く切るのですが、このとき、ウルトラミクロトームという装置を使います。 - 薄切した切片をグリッドに載せます。
- 切片を染色し、乾燥後、検鏡します。
この他、レプリカ法、シャドウイング法や、凍結割断レプリカ法、およびそれらを組み合わせた試料作製法が用いられています。
The sample for TEM observation must be thin enough. The ultrathin sectioning technique used to prepare biological samples is briefly described below.
- Cut out the tissue area to be observed and fix it with glutaraldehyde or osmium tetroxide.
- Dehydrate it with alcohol or acetone to remove water.
- Embed the dehydrated sample in epon or other resin and then slice it thinly to a thickness of less than 0.1 micron.
The embedded block is cut into ultrathin slices, called ultrathin sections, with a glass knife (or diamond knife), that can be carried out by using a device called an ultramicrotome. - Place the ultrathin sections on a grid.
- Stain and dry them.
In addition, replica method, shadowing method, freeze-fracture replica method, or a combination of these methods are used for TEM sample preparation.
SEMの試料作製 SEM sample preparation technique
SEMで試料を観察する場合は、TEMと同様に固定、脱水をおこなった後、臨界点乾燥、自然乾燥等の方法で試料を乾燥します。さらに、試料表面に導電性を持たせるために表面に金や白金などをコーティングします。これには、二次電子の放出効率を上げるという目的もあります。
また、急速凍結法による物理的固定や、凍結した試料をそのまま観察するクライオSEM法を用いることもあります。
The sample for SEM observation must be fixed and dehydrated in the same way as in TEM, and then dried using critical point drying, natural drying, or other methods. In addition, the sample surface is coated with gold or platinum to make it electroconductive. The purpose of doing this is also to increase the efficiency of secondary electron emission.
Physical fixation with quick freezing method or cryo-SEM method, in which frozen samples are observed as they are, may also be used.
利用にあたって Precautions for use
実験実習支援センターには、透過型電子顕微鏡と走査型電子顕微鏡が設置されています。
電子顕微鏡の利用はすべて予約制になっています。透過型電子顕微鏡については、時間単位の予約制になっているため、連続して予約することは控えてください。
電子顕微鏡は利用負担の対象になっており、透過型電子顕微鏡では撮影枚数、走査型電子顕微鏡では利用回数に応じた利用負担が課金されます。
使用中に異常や不審な点があった時には、利用ノートにその旨記入すると共に、担当者まで連絡してください。
The Center is equipped with a TEM and SEMs. All are available for use by booking in advance. TEM is reserved on an hourly basis, and consecutive booking must be discouraged.
Electron microscopes are charged according to use.
If you notice anything unusual or suspicious during use, please note it in the user record book and contact the staff.
設置場所 Location
4階 電子顕微鏡室(401号室)
Electron Microscope Lab (Room #401, CRL 4th floor)
担当者 Contact person
山元 武文(Takefumi Yamamoto)(TEL 2304)
森 康博(Yasuhiro Mori)(TEL 2307)
 前へ BACK 前へ BACK
|
先頭へ TOP
|
Last Updated 2022/12/06